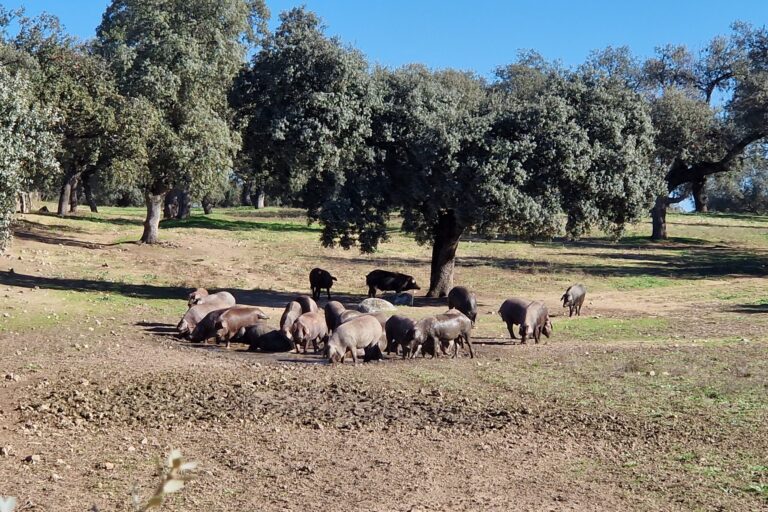
Los Peroches, Spain
Case Study site features
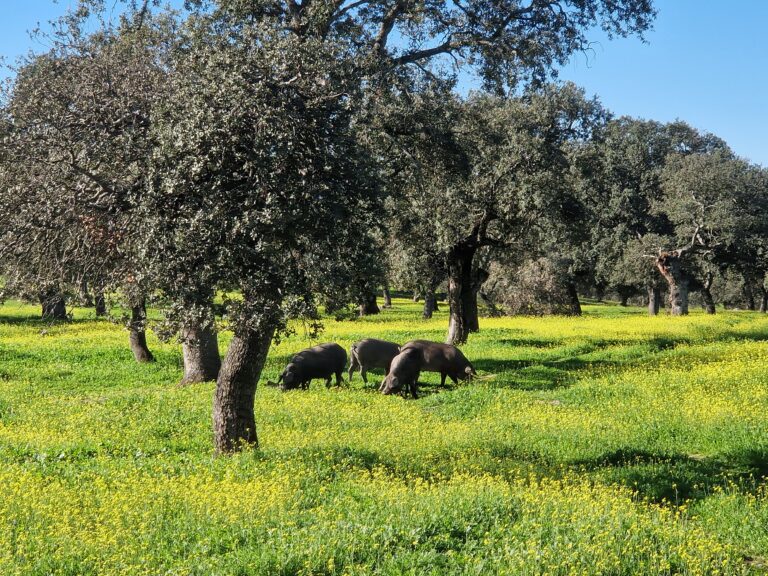
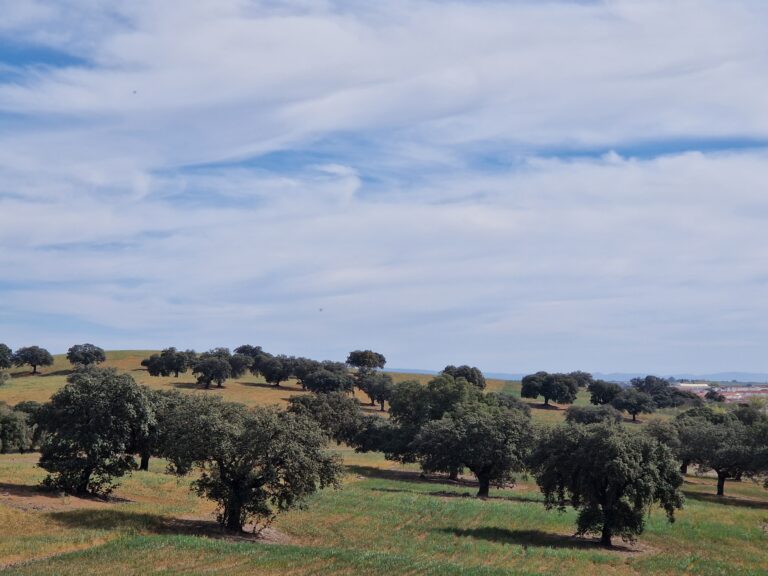
Los Pedroches is located in Córdoba Province, Andalusia, in southern Spain, at an elevation ranging from 350 to 850 m above sea level. The region has a striking landscape dominated by the Dehesa, a unique Mediterranean symbiotic ecosystem of livestock and forests. Spanning over 360 thousand hectares, it is the largest in the world, characterized by a diverse array of Quercus species (oak trees and shrubs) and the traditional symbiosis between nature and agricultural practices.
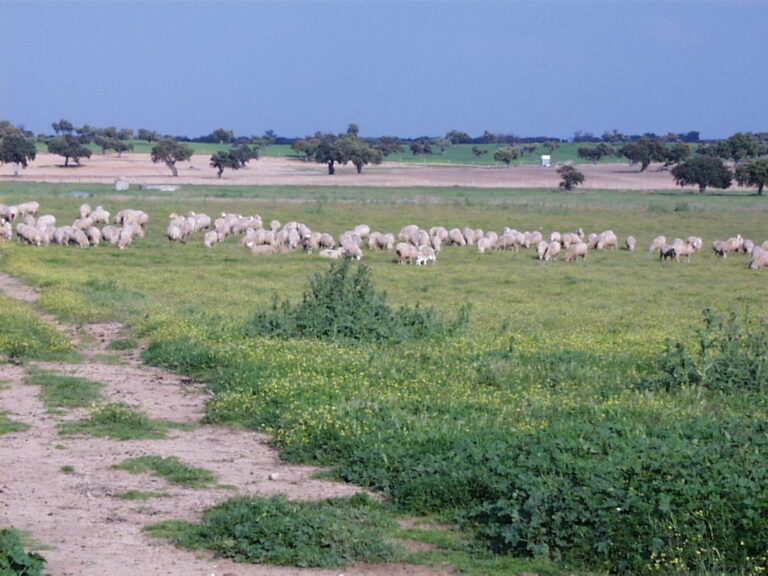
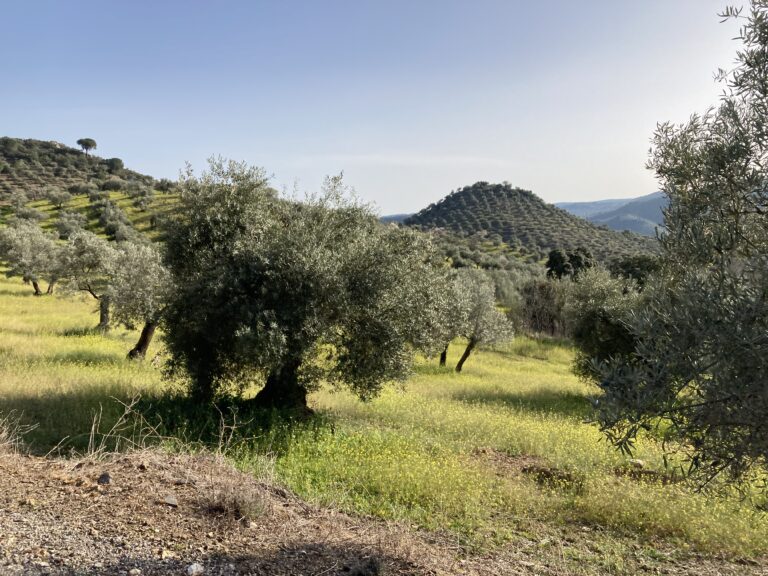
Land use in Los Pedroches includes rainfed crops such as cereals and olive trees, alongside livestock farming. The dehesa serves as a base of sustainable land management in the region.
The climate is typically Mediterranean, with a mean annual temperature of 17 °C. Average annual precipitation is 600 mm, while the evapotranspiration rate reaches 1,180 mm, highlighting the need for efficient water management to sustain the delicate balance of this iconic ecosystem.
- Aridity index:
- Key drivers of LDD:
- Solutions:
- Type of implemented solutions:
- The participatory approach:
- Key stakeholders involved:
0.45 indicating Semi-Arid Climate
Aridity Index (AI) is a measure used to assess the dryness of a region by comparing the amount of precipitation (rainfall) to potential evapotranspiration (the water loss from soil and plants).
Aridity Index is calculated as the ratio of annual precipitation to potential evapotranspiration.
Lower values indicate drier conditions, with very low values representing arid or desert-like environments.
The aridity index is essential in climate studies, water management, and agriculture, as it helps classify climates and assess water availability.
For Los Pedroches LDD drivers are predominantly drought, climate change, land use intensification leading soil fertility loss, land abandonment, soil erosion and overgrazing.
LDD drivers
Land degradation and desertification drivers are factors that lead to land deterioration and loss of productivity.
LDD drivers include natural causes, drought, and human activities, such as deforestation, overgrazing, and unsustainable farming. These drivers reduce soil fertility, increase erosion, and harm vegetation, making land more prone to degradation.
Conservation Agriculture Practices
Examples: No-tillage, green cover, crop rotation, agroforestry.
Innovative Grazing Management
Examples: Rotational grazing, silvopasture (integration of trees, pasture, and livestock on the same land), stock density management, virtual fencing.
Use of Organic Fertilizers
Examples: Composting, manure application, biofertilizers, vermicomposting.
Restoration of Natural Ecosystems and Agroecosystems
Examples: Reforestation and afforestation, wetland restoration, pollinator habitat creation, soil rehabilitation.
Nature-Based Solutions
(NBS)
Nature-based solutions use natural processes and ecosystems to address challenges like climate change and land degradation.
Examples include reforestation and cover cropping, which improve environmental resilience and provide benefits like water filtration and habitat preservation.
Co-Design (CoD)
Co-design involves stakeholders working together to plan and create solutions, ensuring that local needs, knowledge, and values shape the outcome. This fosters community ownership and relevance of the solution.
Co-Implementation (CoI)
Co-implementation is the shared execution of a plan by stakeholders, with each actively participating in putting the solution into action. This approach builds capacity and strengthens commitment to the project’s success.
Co-Assessment (CoA)
Co-assessment is the joint evaluation of project outcomes by stakeholders to measure effectiveness and identify improvements. It encourages adaptive management and maintains accountability and transparency.
The OLIPE Cooperative
COVAP Cooperative
Andalusian Environmental Information Network – REDIAM
Sierra de Cardeña and Montoro Natural Park
Andalusian Institute of Agricultural and Fisheries Research and Training – IFAPA
Agrifood Research Center – CICAP
Pedroches Cooperative
OLIPE Cooperative
Olivarera Na. Señora de la Luna
Dehesas Cordobesas CORPEDROCHES
Centro Universitario de Desarrollo Agroalimentario de Los Pedroches – CUDA









